whats is the silicon carbide rods ?
Introduction to silicon carbide rods:
Silicon carbide ( SiC ) electric heating element is a rod-shaped non-metal high temperature electric heating element made of green high-purity hexagonal silicon carbide as the main raw material , processed into billet, high temperature silicidation, and recrystallized at a high temperature of 2200 °C . The normal use temperature can reach 1450 ℃ . Under reasonable use conditions, it can be used continuously for more than 2000 hours . When used in the air , it does not require any protective atmosphere . Long, slightly deformed, easy to install and maintain. Therefore , it is widely used in multiple high-temperature furnaces and other heating equipment in industries such as electronics, magnetic materials, powder metallurgy, ceramics , glass, metallurgy and machinery . In addition to the difference in intrinsic quality, the service life of the silicon carbide rod heating element is also affected by the use temperature of the element, the surface load of the heating part of the element , the ambient atmosphere, harmful substances, the power supply method (intermittent and continuous use ) and the use of the element. Factors such as series-parallel mode affect the use load of components at each temperature .
Properties of silicon carbide rods ( SiC ):
The element is hard and brittle, has a small expansion coefficient, can withstand rapid cooling and rapid heating , is not easy to deform , has good chemical stability, strong acid resistance, does not react with strong acids , and has poor alkali resistance . It can be corroded, decomposed and heated at high temperatures. element . Chlorine can decompose components , and hydrogen and nitrogen have different degrees of erosion. If it is used in air and water vapor for a long time , the components will age slowly, the content of silica will increase , the resistance value will increase , and the following reactions will occur:
S iC+2O2= S iO2+CO2
S iC+4H2O= S iO2+H2+CO2
The resistance value of the silicon carbide rod changes with the temperature of the element , because the element is a nonlinear resistor. From room temperature to 850±50℃ , the resistance changes from large to small, and above 850±50℃ , it changes from small to large . That is to say : the components will slowly age, the silicon dioxide content will increase, the resistance value will increase, and the following reactions will occur:
SiC+2O2=SiO2+CO2
SiC+4H2O= SiO2+4H2+CO2
The resistance value of the silicon carbide rod changes with the temperature of the element, because the element is a nonlinear resistor. From room temperature to 850±5℃ , the resistance changes from large to small, and above 850±5℃ , it changes from small to large . That is to say : the temperature coefficient of resistance of the element has a negative stage and a positive stage. The resistance marked at one end of the rod is measured at 1050±50℃ according to the ministerial standard , which is convenient for installation.
element is closely related to the temperature of the furnace and can be adjusted arbitrarily as needed. When the furnace temperature is high, the load density should be increased, otherwise, the load density can be reduced. The so-called "adjustment".
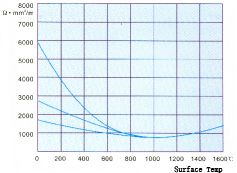
Resistance temperature characteristic curve of silicon carbide rod
It can be seen from the figure that the resistance of the heating element is concave and curved . When the temperature is about 850 +50 ℃ , the resistivity is the smallest. After this temperature point, the resistivity increases correspondingly with the increase of temperature. When the temperature exceeds 1500 ℃ , the aging speed is accelerated, and the components are rapidly burned.












 E-mail:web@kejiafurnace.com
E-mail:web@kejiafurnace.com
 Tell:+(86) 18037178440
Tell:+(86) 18037178440
 Whatapp:+(86) 180-3717-8440
Whatapp:+(86) 180-3717-8440
 Address:Room 1505, Building 9, No. 26 Dongqing Street, Zhengzhou High-tech Industrial Development Zone
Address:Room 1505, Building 9, No. 26 Dongqing Street, Zhengzhou High-tech Industrial Development Zone
